by DrCiuffo | Jul 15, 2022 | Blog, Articles, Heart Health
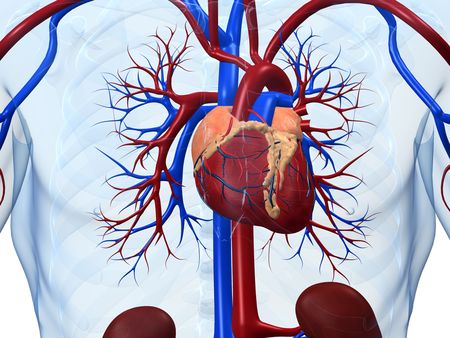
Anatomy of the Heart As one of the most essential parts of the body, the anatomy of the heart is important to know and understand. The heart is located just behind the sternum, slightly to the left. It’s protected by a tough sac called the pericardium. The heart... by DrCiuffo | Feb 5, 2020 | Articles, Blog, Dr. Giovanni B Ciuffo, Heart Health, Heart Surgery, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgeons, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery, Uncategorized
What is a Pulse Deficit? The concept of a pulse deficit can be both confusing and frightening if you’re not a member of the medical community, but it has a direct bearing on the health of your heart and can be life threatening if not treated properly and allowed to... by DrCiuffo | Jan 30, 2020 | Articles, Blog, Dr. Giovanni B Ciuffo, Heart Health, Heart Surgery, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgeons, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery, Uncategorized
LIMA LAD is a life-saving procedure for your heart. What LIMA LAD does is open your heart’s blood flow by involving two different arterys. These are the left internal mammary artery and the left anterior descending artery, or LIMA LAD for short. This minimally... by DrCiuffo | Sep 4, 2019 | Coronary Surgery, Articles, Blog, Dr. Giovanni B Ciuffo, Heart Health, Heart Surgery, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgeons, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery, Recovery, Uncategorized
Heart surgery is one of the most sophisticated and complex types of surgery. It is demanding and requires an excellent team of physicians, assistants, and support personnel. Minimally invasive heart surgery significantly decreases the amount of trauma and damage to... by DrCiuffo | Aug 3, 2019 | Coronary Surgery, Articles, Blog, Dr. Giovanni B Ciuffo, Heart Health, Heart Surgery
Although some have described cardiac surgery as a dying specialty, that couldn’t be farther from the truth. Cardiac surgery today is seeing astronomical growth with innovations in minimally invasive procedures. Therefore, cardiac surgery is not sliding into... by DrCiuffo | Mar 15, 2019 | Coronary Surgery, Articles, Blog, Dr. Giovanni B Ciuffo, Heart Health, Heart Surgery, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgeons, Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery, Uncategorized
Minimally invasive heart surgeons perform procedures that cause less trauma and pain, resulting in quicker recovery times compared to open-heart surgery. These surgeons perform procedures using small incisions in your chest as a safer alternative to open-heart...

